Nurturing Executive Functioning in K-12 Students: Scoutlier’s Strategies for Success
Written by Kiara Klein, Director of Programs, Scoutlier by Aecern
Executive functioning skills are integral to academic success, as they serve a vital role in every subject. From reading comprehension and mathematical problem-solving to conducting research and writing essays, students rely on executive functioning skills to navigate complex tasks and achieve academic milestones.
Like skilled gardeners nurturing delicate seedlings, K-12 educators cultivate the growth of their students’ executive functioning skills by providing the essential care and guidance needed for them to flourish. Although some days the gardening may feel like it’s happening in a tornado of outbursts, disruptions, and distractions.
So in the classroom where every day brings different “weather,” how can you help impart these essential skills, aiding in your students’ growth of their full potential? Well, it comes down to strategy and helping your students develop the skills for success.
Understanding Executive Functioning
The term “executive function” is outlined by one’s cognitive process around setting and achieving goals, and staying on task despite disruptions and distractions. Executive function skills are honed and developed through time and experience. No one is born with the innate ability to prioritize tasks, control impulses, stay focused and plan ahead.
These vital skills form the cornerstone of navigating life’s complexities, including the demands of work, academics, parenting, relationships, and the myriad responsibilities of a bustling lifestyle. They empower us to prioritize effectively, adapt to unforeseen challenges, and exercise restraint in the face of impulses, ensuring we stay on course toward our goals.
Executive functioning skills are regulated by the prefrontal cortex, a region of the brain responsible for our cognitive functions, including planning, decision-making, impulse control, and working memory. Neuron pathways in the brain play a crucial role in the development and refinement of these skills through a process known as neural plasticity.
Neural plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize and adapt its structure and function in response to learning, experience, and environmental stimuli. As individuals engage in various cognitive tasks and experiences, neuron pathways in the prefrontal cortex become strengthened or weakened based on the frequency and intensity of neuronal activity.
During childhood and adolescence, when executive functioning skills are still developing, the brain undergoes significant changes in structure and connectivity. Neuron pathways associated with executive functions are gradually refined through repeated practice, exposure to challenging tasks, and the acquisition of new knowledge and skills.
For example, when a child engages in tasks that require planning and problem-solving, such as organizing a project or strategizing during a game, specific neuron pathways in the prefrontal cortex become activated. Through repeated engagement in these tasks, the connections between neurons involved in executive functioning strengthen, resulting in more efficient neural networks dedicated to these skills.

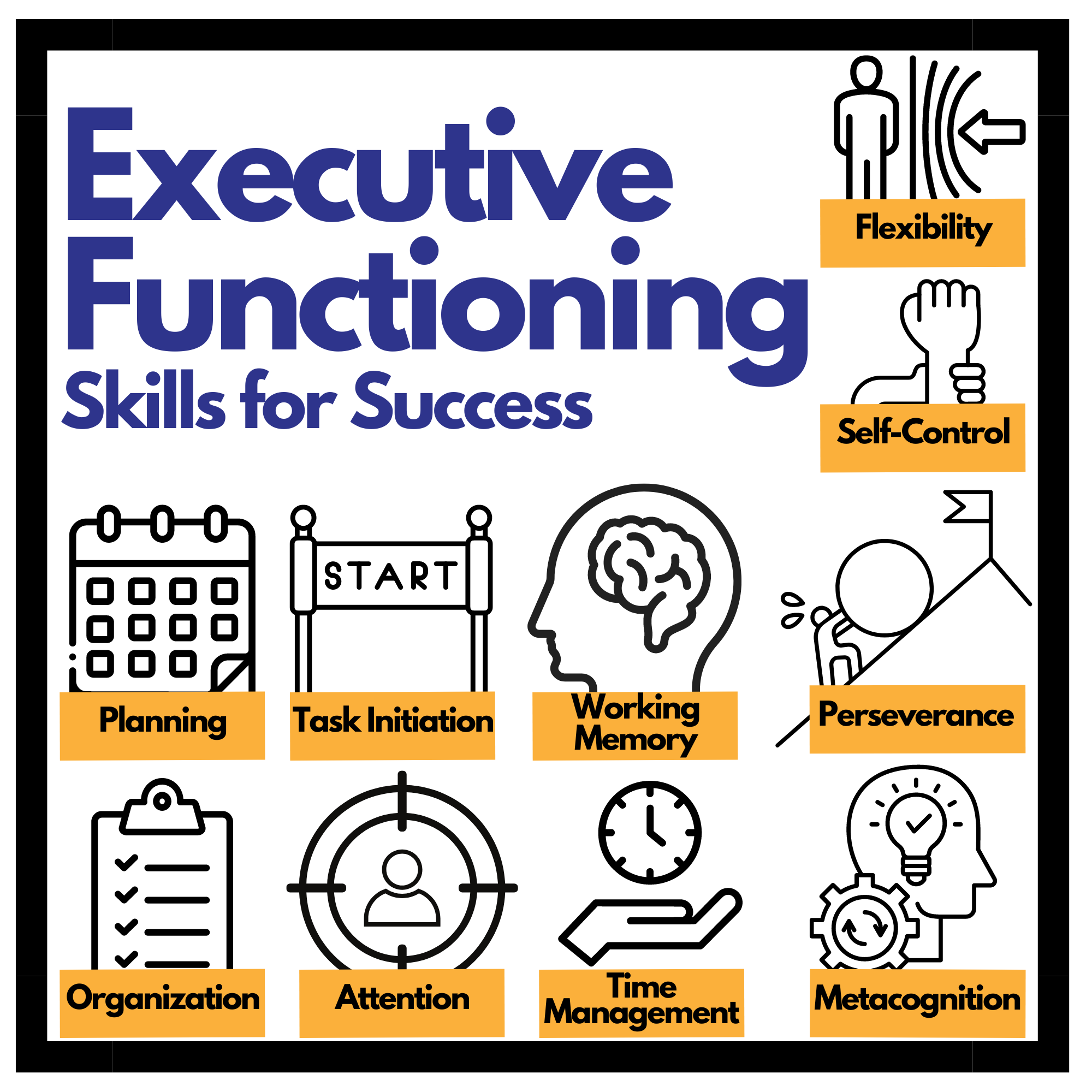
The Core Skills
There are some core skills that help with the process of executive functioning, and these skills can be honed to help your students improve their academic performance and complete learning tasks.
Flexibility: The ability to adapt to changing situations, perspectives, or demands and adjust one’s responses or strategies accordingly.
Self-control: The capacity to regulate one’s thoughts, emotions and behaviors in order to achieve goals, resist impulses, and maintain focus.
Planning: The process of setting goals, developing strategies, and organizing steps to accomplish tasks or achieve set objectives.
Task Initiation: Beginning tasks and activities without procrastination, hesitation or avoidance.
Working Memory: The cognitive system responsible for temporarily storing and retrieving the information needed for tasks, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Perseverance: Persisting in the face of obstacles, setbacks, or challenges, while maintaining effort and motivation toward achieving long-term goals.
Organization: arranging and structuring materials time or information in a systematic and orderly manner.
Attention: Sustained mental focus, and the ability to concentrate on relevant tasks and goals
Time Management: The ability to allocate and prioritize time, set realistic deadlines, and balance competing demands to accomplish tasks.
Metacognition: Awareness and understanding of one’s cognitive processes, including knowledge about how to plan, monitor, and evaluate thinking and learning strategies.
Strengthening these skills through practice, teaching strategies like scaffolding, and supportive tech tools like Scoutlier, can enhance the student’s ability to navigate multi-step directions, solve bigger problems, and achieve overall success. Working on your students’ executive functioning will help them to maintain their composure and solve more complex problems and help them to become better learners.
Scoutlier Supports Executive Functioning Skills
Organization
Assignments, projects and resources in Scoutlier are organized in a structured and accessible way. Digital folders categorize and store materials to related subjects and lessons. Students can easily find the required materials which helps them stay on task by keeping the digital environment orderly.
Planning and Task Management
Scoutlier empowers educators to break down lessons into manageable tasks and guides educators through the lesson creation process in a way that ensures structured and accessible lessons. These lessons are broken down into task-by-task, step-by-step prompts. This presentation allows students to focus on one thing at a time, decreasing chances of overwhelm and increasing follow through on tasks.
Cognitive Flexibility
Scoutlier supports collaborative learning experiences that encourage students to engage with the perspectives, ideas, and problem-solving processes of their classmates. By participating in collaborative/group projects and activities, students can strengthen their working memory through new information and adapt their thinking based on feedback and input from peers.
Metacognitive Reflection
Scoutlier encourages metacognitive reflection through reflection self-assessment prompts. By reflecting on their learning experiences, identifying strengths and areas of improvement, and setting goals, students can enhance their awareness of their cognitive processes and self-directed learning.
Funded by grants from the National Science Foundation and other federal agencies, Scoutlier provides a free platform and free content that inspires students to learn and helps teachers scaffold and differentiate instruction. Whether you’re teaching a small STEM program or an overcrowded English classroom, Scoutlier can help you reach your students in new and engaging ways! Sign up for your FREE teacher account today.
RESOURCES






